Research
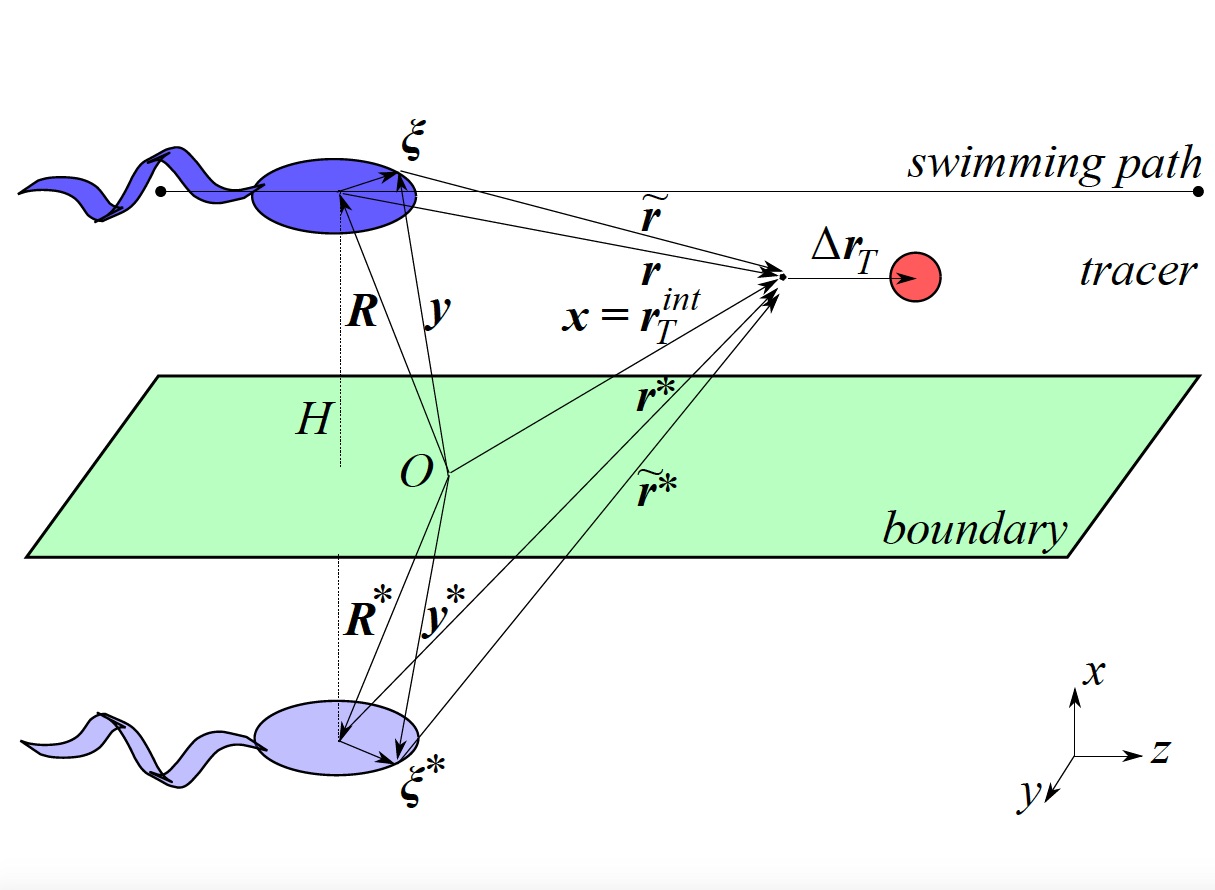
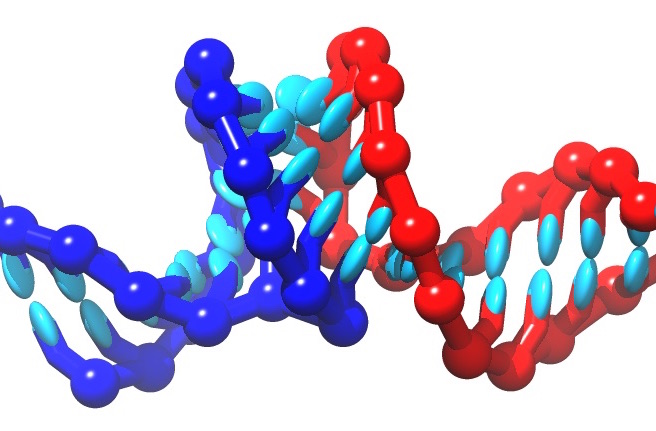
Liquid crystals, DNA and Biopolymers
Long molecules with functions
from transferring genetic information to displays.
Surfaces and Interfaces
Micro-patterned and soft surfaces with relevance to friction, lubrication, waterproofing and de-icing.
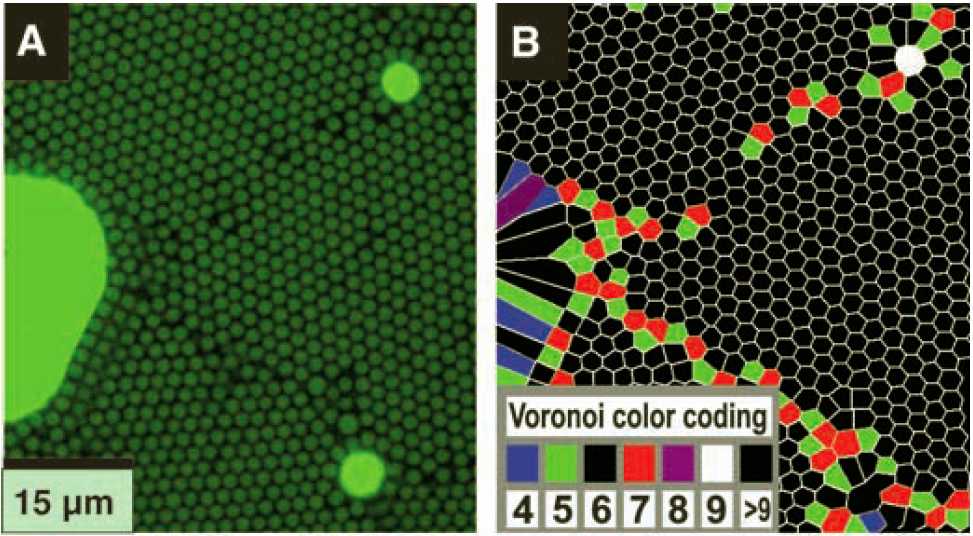
Powders, Grains and Gels
Theory of elastic surfaces, imaging grain boundary dynamics, and applications to batteries and engine oil.
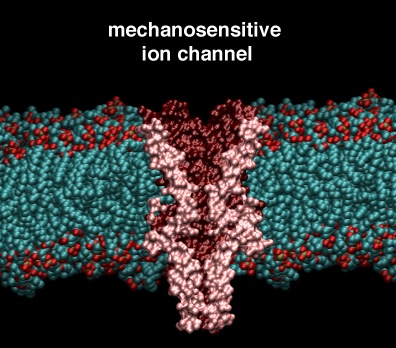
Membranes
From modelling ion transport across biological membranes to designer membranes for fuel-cell applications.